Summary:
Matter can be a
- homogeneous or
- heterogeneous
substance. A homogeneous substance can be either pure or a mixture (solution). A
pure substance can be a compound or an element.
The composition of mixtures is
given by mass and molar concentrations (omega A
, cA) related to the unit volume ( omegaA
[kg.m-3], cA [mole.m-3]), where 1 mole means 6.1023 particles (molecules). Mass or
molar fractions ( omegaA [kg A/kg mixture], xA [mole A/mole of mixture]) are
dimensionless.
Molecules of compounds consist of atoms, which have a nucleus
(protons+neutrons) and an electron shell. Atomic number Z is the number of protons
(=number of electrons). Atomic mass is the mass of protons and neutrons in the
nucleus (mass of 1 proton = mass of 1 neutron = 1 amu). Isotopes are elements with
the same atomic number but different atomic mass (a different number of neutrons).
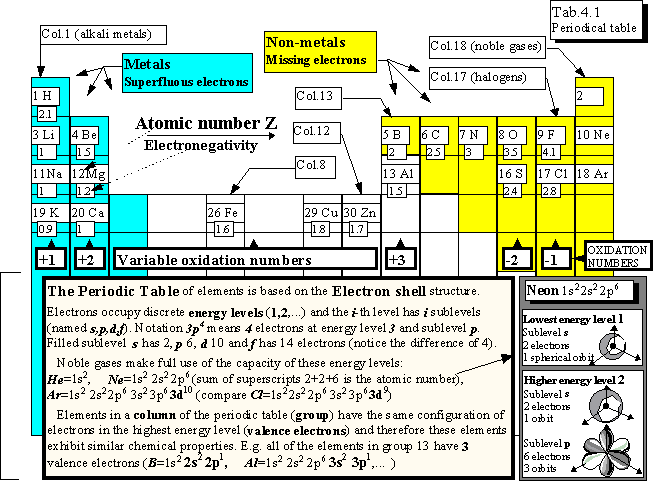
Elements are arranged according to their atomic number in the periodic table
of elements (increasing Z in rows). The ability of elements to form a compound is
determined by the number of electrons at the highest energy level (valence
electrons). The elements with the same number of valence electrons and similar
chemical behaviour are arranged in columns.
Bonds can be - ionic (attraction of
cations /+/ and anions /-/), or
- covalent (sharing electrons by two atoms in a
molecule).
The oxidation number is equivalent to the electrical charge of the ion.
Covalent bonds between atoms with different electronegativity are unsymmetric
(polar bonds). Even molecules containing polar bonds can be considered nonpolar
from outside, if they are symmetric and the gravity centres of positive and negative
charges coincide (e.g. CH4 ). H2 O is a polar molecule, because the two hydrogen
atoms are arranged unsymmetrically. Some polar molecules dissociate in liquids to
independently moving cations (+) and anions (-), e.g. 10-7 moles of H2 O molecules
dissociate to H + (free proton) and (OH) - in 1 litre of neutral water.
The molar
concentration of protons is expressed by a pH value,
pH= -log [H + ]
and pH=7 in
neutral water. Acids increase the concentration of protons (pH<7), while bases cause
a decreasing concentration of H+ (pH>7).
Mass balancing of a black box can be based upon three kinds of equations:
1.
conservation of total mass,
2. conservation of mass of individual elements,
3.
stoichiometry of chemical reactions and balance of mass flow-rates of compounds
(stoichiometry and actual yield of reactions enable us to compute the production
rates of compounds).
·
@TEC: 3. 3.2003
Change language to


 peoples
peoples


 mailto: Zitny
mailto: Zitny
