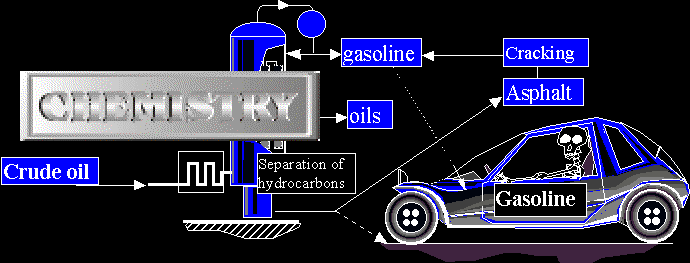
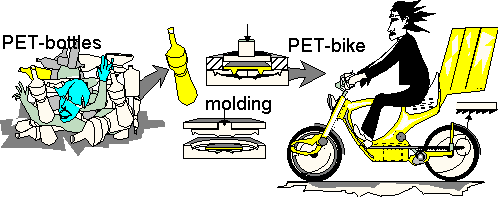
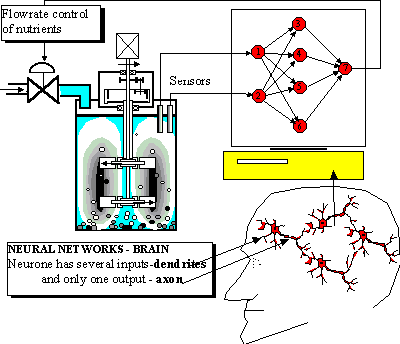
Mass and moles, structure of matter [Summary].
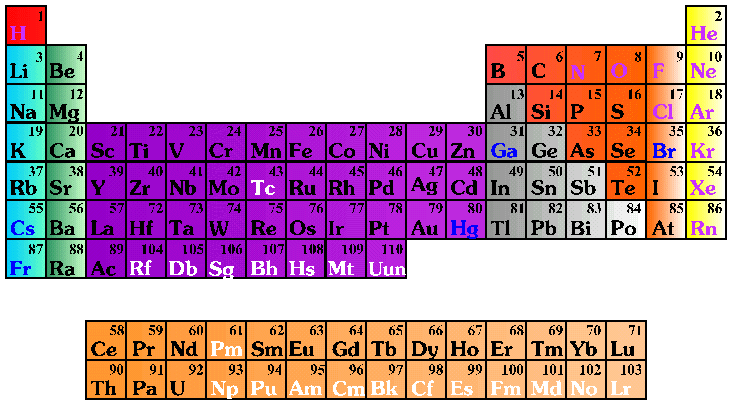
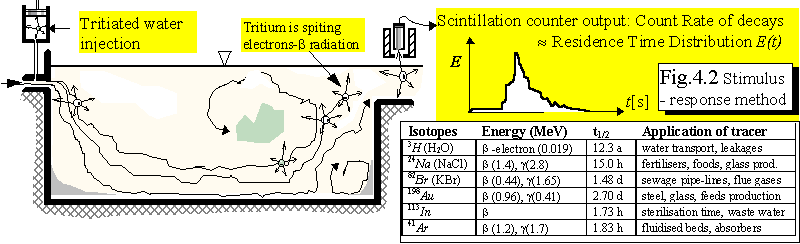
- Atomic mass, isotopes (atomic structure)
.
- Molecular mass, molecular structures,
periodical table [link to WEB-ELEMENTS, Sheffield]
,
bonding (ionic and covalent bonds),
compounds (table of selected compounds).
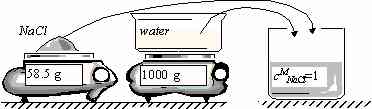
- Concentrations (mass and molar concentrations, mass and molar fractions)
- Mass balance (mass balances of compounds and elements, example: burner).
- Stoichiometry of chemical reactions.
 |
![Kekule (song)]() It was not and is not easy to identify the correct structures,
given only the summary chemical formulas. For example the structure of benzene,
C6H6, remained a puzzle for a long time, though four possible
arrangements with open-end molecules were suggested. None of them could explain
some peculiarities of benzene (for example the non-existence of
C6H5Cl isomers), until the chemist August Kekul‚ (1858)
found the explanation while staring into his fireplace:
"...Again the atoms were gamboling before my eyes.
My mental eye, rendered more acute by repeated visions of the kind,
could now distinguish larger structures of manifold conformations;
long rows, sometimes more closely fitted together, all twining and twisting
in snake-like motion. But look! One of the snakes had seized hold of its own
tail, and the form whirled mockingly before my eyes. As if by a flash of
lightning I awoke; and this time also I spent the rest of the night in
working out the consequences of the hypothesis."
But Kekul‚ also added:
"Let us learn to dream, gentlemen, then perhaps we shall find the truth.
But let us beware of publishing our dreams till they have been tested by the
waking understanding"
It was not and is not easy to identify the correct structures,
given only the summary chemical formulas. For example the structure of benzene,
C6H6, remained a puzzle for a long time, though four possible
arrangements with open-end molecules were suggested. None of them could explain
some peculiarities of benzene (for example the non-existence of
C6H5Cl isomers), until the chemist August Kekul‚ (1858)
found the explanation while staring into his fireplace:
"...Again the atoms were gamboling before my eyes.
My mental eye, rendered more acute by repeated visions of the kind,
could now distinguish larger structures of manifold conformations;
long rows, sometimes more closely fitted together, all twining and twisting
in snake-like motion. But look! One of the snakes had seized hold of its own
tail, and the form whirled mockingly before my eyes. As if by a flash of
lightning I awoke; and this time also I spent the rest of the night in
working out the consequences of the hypothesis."
But Kekul‚ also added:
"Let us learn to dream, gentlemen, then perhaps we shall find the truth.
But let us beware of publishing our dreams till they have been tested by the
waking understanding"
|
|